GoPlus has detected unusual authorizations linked to 402bridge, leading to more than 200 users losing USDC in excessive authorizations made by the protocol.
Summary
- The x402bridge protocol suffered a breach caused by a leaked admin private key, allowing an attacker to steal about $17,693 in USDC from over 200 users.
- The hack reveals vulnerabilities related to the x402 mechanism which relies on private keys stored on a server to enable admin privileges to on-chain addresses that may distribute and authorize transactions excessively.
On Oct. 28, the web3 security company GoPlus Security’s Chinese social media account alerted users of a suspected security breach involving the x402 cross-layer protocol, x402bridge. The hack occurred just days after the protocol was launched on-chain.
Before minting USDC (USDC), the action must first be authorized by the Owner contract. In this case, excessive authorizations led to more than 200 users losing their remaining stablecoins in a series of transfers.
GoPlus (GPS) noted that the creator of the contract beginning with 0xed1A made an ownership transfer to the address 0x2b8F, granting the new address special administrative privileges held by x402bridge team, such as the ability to modify key settings and move assets.
Shortly after gaining control, the new owner address executed a function called “transferUserToken.” This function allowed the address to drain all remaining USD Coins from wallets that had previously granted authorization to the contract.
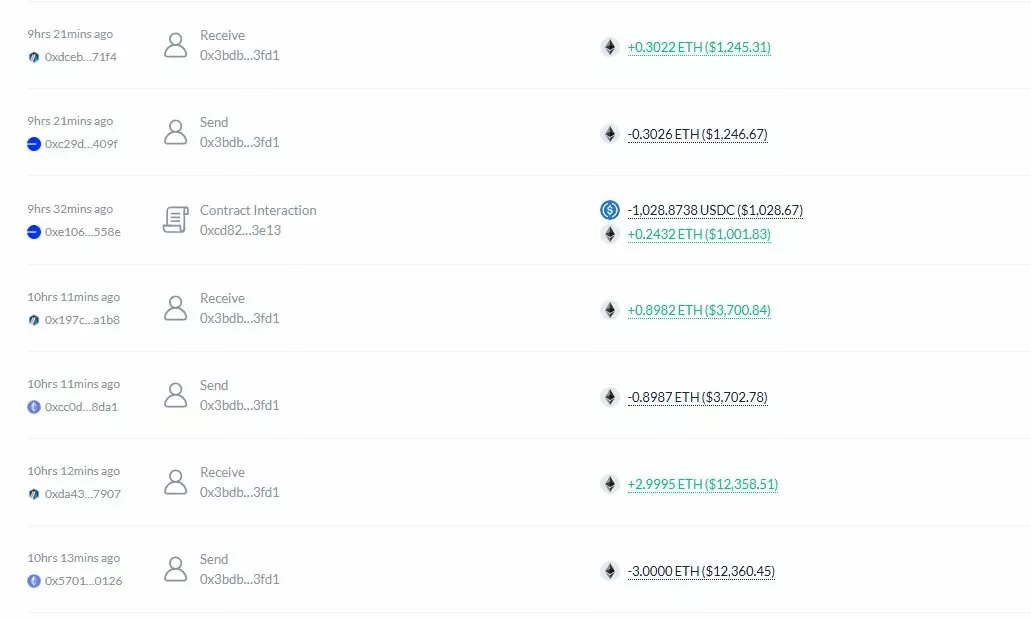 402bridge suffered a breach that led to the hacker draining USDC from user wallets | Source: GoPlus Security
402bridge suffered a breach that led to the hacker draining USDC from user wallets | Source: GoPlus SecurityIn total, the 0x2b8F address drained about $17,693 worth of USDC from users before exchanging the stolen funds into ETH. The newly-converted ETH was later transferred to Arbitrum through multiple cross-chain transactions.
As a result of the breach, GoPlus Security recommended users who hold wallets on the protocol to cancel any ongoing authorizations as soon as possible. The security firm also reminded users to check whether the authorized address is the official address of the project before approving any transfers.
In addition, users are encouraged to only authorize the necessary amount and never grant unlimited authorizations to contracts. Overall, they are urged to regularly check authorizations and revoke unnecessary ones.
The hack occurs just a a few days after x402 transactions began seeing a boom in usage. On Oct. 27, the market value of x402 tokens surpassed $800 million for the first time. Meanwhile, Coinbase’s x402 protocol recorded 500,000 transactions in a single week, indicating a 10,780% increase compared to the previous month.
The x402 protocol enables both humans and AI agents to make transactions using HTTP 402 Payment Required status code to enable instant, programmatic payments for APIs and digital content. This means that they can make instant stablecoin payments over HTTP.
What caused the alleged hack on 402bridge?
On-chain sleuths and blockchain security firms like SlowMist have concluded that the breach was most likely caused by a private key leak. However, they did not rule out the possibility of insider involvement. Due to the breach, the project has halted all activity and its website is now offline.
The official account for 402bridge has since addressed the exploit, confirming that it was indeed caused by a private key leak which led to more than a dozen team test wallets and main wallets on the protocol getting compromised in the process. The team is currently investigating the incident and has reported it to the authorities.
“We have promptly reported the incident to law enforcement authorities and will keep the community informed with timely updates as the investigation progresses,” said 402bridge.
In a separate post that was shared earlier, the protocol explained how the x402 mechanism works. It requires users to sign or approve transactions via the web interface. The authorization is then sent to a back-end server that extracts the funds and mints the tokens.
“When we onboard to x402scan.com, we need to store the private key on the server in order to call contract methods,” said the protocol.
“This step may expose admin privileges because the admin private key is connected to the internet at this stage, potentially leading to a leak of permissions,” the team continued.
As a result, if the private key is stolen by a hacker, then they are able to take over all admin privileges and reassign user funds to the hacker’s contract.















 English (US) ·
English (US) ·